Nexus3 is an open source repository manager designed to store and manage software artifacts. It serves as a central hub for developers to store, retrieve, and distribute components, binaries, and dependencies used in their projects. Nexus3 helps in improving the efficiency of software development by providing a reliable and scalable infrastructure for managing artifacts across different development environments.
Sign in
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.
When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your username and password and click the "Sign in" button.
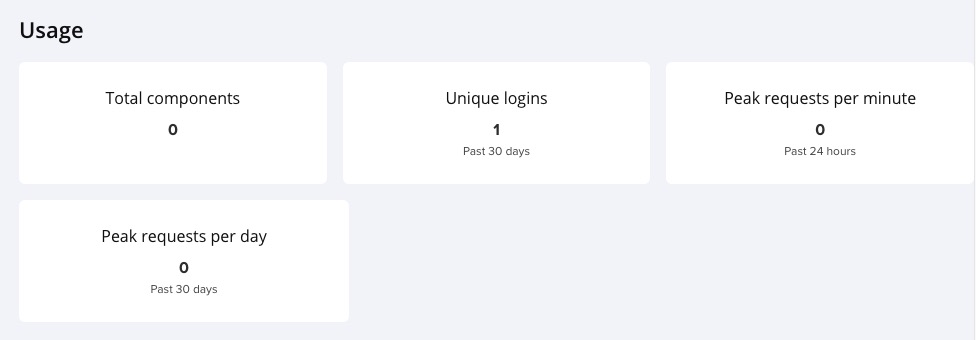
Usage
Usage in Nexus3 provide a visual representation of the usage statistics of your repositories. They can display various metrics such as the number of components or artifacts stored, the storage space used, the number of download requests, and more. These dashboards can help you monitor the activity and health of your repositories, identify trends, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and capacity planning. You can access the usage dashboards from the "Usage" section of your Nexus3 dashboard.
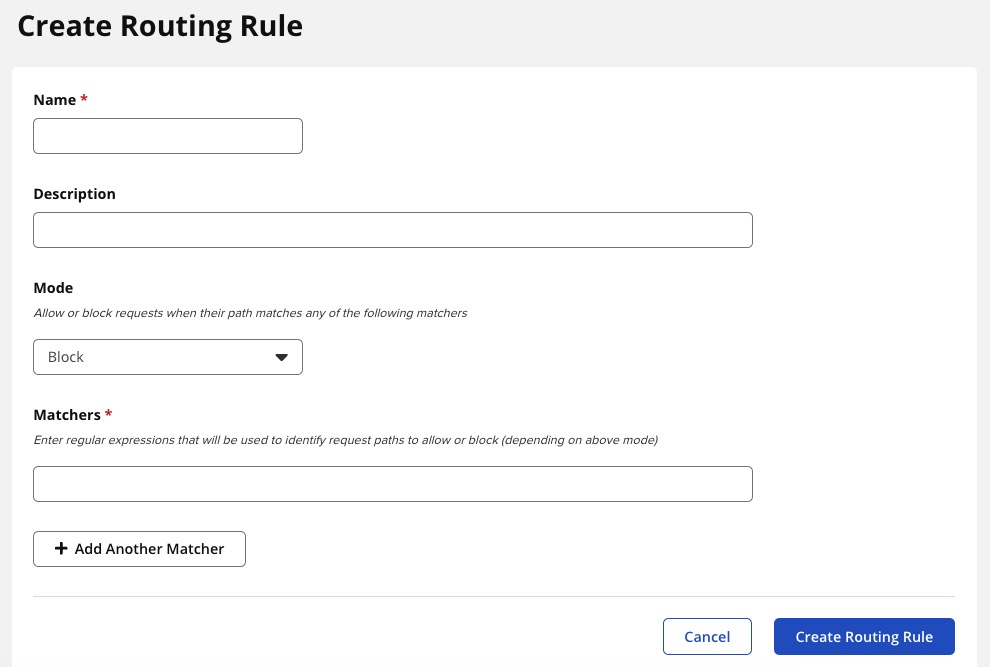
Creating Routing Rule
Routing Rules in Nexus3 Repository Manager are a set of rules that determine how requests to repositories are handled. They provide a way to filter and redirect requests based on the requested path. You can create a routing rule to block certain paths or file types, or to redirect requests to a specific location. This can be useful for managing access to your repositories, optimizing performance, or implementing custom workflows. Routing rules are defined using a simple pattern matching syntax, and can be applied to any repository in Nexus. Once a routing rule is created, it can be assigned to a repository via the repository's configuration settings.
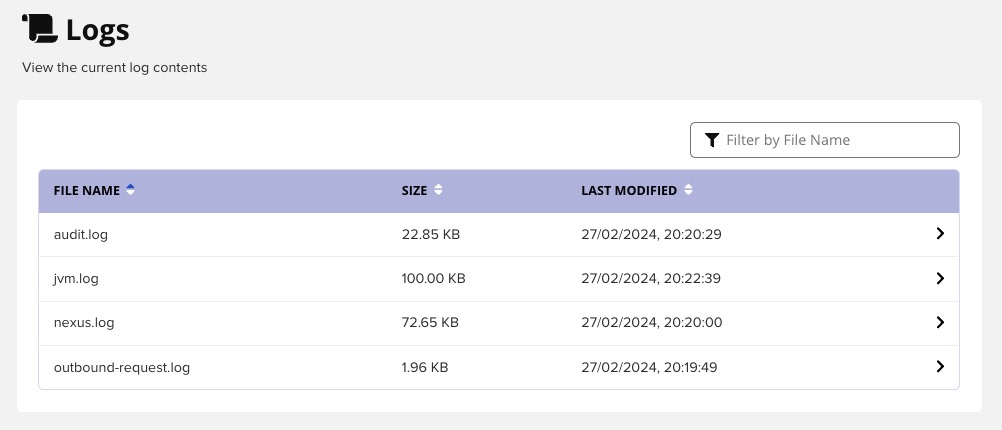
Privileges
Privileges in Nexus3 are permissions that determine what actions a user or role can perform. They provide a way to control access to the various features and functions of Nexus. Privileges can be assigned to individual users or to roles, which are groups of privileges that can be assigned to users. This allows you to manage access control in a flexible and granular way. Nexus provides a set of built-in privileges for common actions like viewing, creating, updating, and deleting components and repositories. You can also create custom privileges to suit your specific needs. Once privileges are assigned, Nexus enforces them by only allowing users to perform the actions that their privileges permit. This helps to ensure that users can only access the data and functionality they need, enhancing the security of your repositories.
Status
Node Status in Nexus3 provides information about the current state of a node in a Nexus cluster. In a multi-node Nexus setup, each node in the cluster can have its own status. The Node Status can provide information such as whether the node is online or offline, its system health, memory usage, disk usage, network status, and other operational details. This information can be useful for monitoring the health and performance of the Nexus cluster, troubleshooting issues, and managing resources.
Cleanup Policies
Cleanup Policies in Nexus3 are rules that automatically remove unused or old components from your repositories. They help manage storage space and keep your repositories clean and efficient. A cleanup policy consists of a set of criteria that components must meet to be eligible for deletion. These criteria can be based on the component's age, usage, or other attributes. You might create a cleanup policy that removes components that have not been downloaded for a certain period of time. Once a cleanup policy is defined, it can be applied to one or more repositories. The cleanup process is then run periodically (as configured), and any components that meet the policy's criteria are removed.
Logs
Logs in Nexus3 are records of events or actions that occur within the system. They provide detailed information about the operation of Nexus, including system messages, error messages, and debugging information. Logs can be used to troubleshoot issues, monitor system activity, and understand the behavior of Nexus. They can include information such as the time of the event, the component or module that generated the log, the level of the log (such as INFO, WARN, or ERROR), and a message describing the event. Nexus logs are written to files on the server where Nexus is running, and can be viewed using a text editor or a log viewing tool. The location and format of the log files, as well as the level of detail included in the logs, can be configured in the Nexus settings.
Create Role
Roles in Nexus Repository Manager 3 are a way to group related privileges together. A role represents a certain level of access or a set of permissions that can be assigned to a user or a group of users. Roles make it easier to manage access control in Nexus, especially in larger organizations with many users. Instead of assigning individual privileges to each user, you can assign roles that include the necessary privileges. If you need to change the access level for a group of users, you can simply update the role, and the changes will apply to all users with that role.
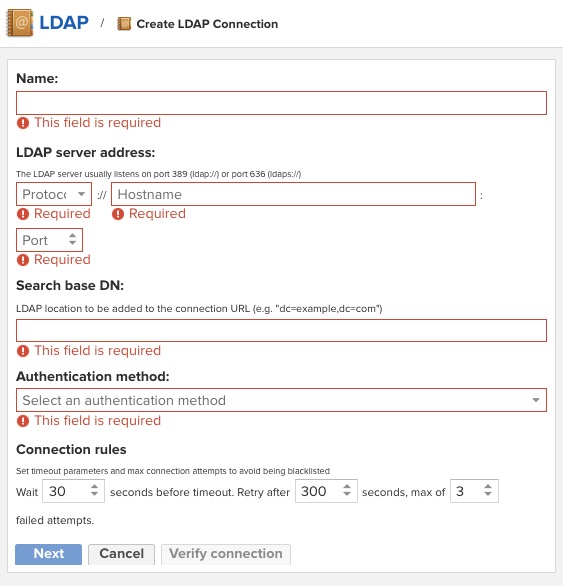
Creating LDAP
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) in Nexus3 is a protocol used to access and maintain distributed directory information services over a network. Nexus supports LDAP integration, which allows you to use an external LDAP server (like Microsoft Active Directory or OpenLDAP) for user authentication and authorization. With LDAP integration, you can manage Nexus users and roles in your existing LDAP server, rather than managing them directly in Nexus. This can simplify user management, especially in larger organizations, and allows you to leverage existing infrastructure and processes.