Bytebase is an open source collaborative database management platform designed to simplify the process of database development and administration. You can use Bytebase as a developer, database administrator, or part of a cross-functional team. It provides a centralized hub for efficient collaboration, making it easier to design, document, and evolve your databases.
Sign In
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.

When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your username and password and click the "Sign In" button.
Issues
In Bytebase, issues typically refer to problems, tasks, or topics that need attention or resolution within the collaborative database management platform. Users can create issues to track and manage various aspects of database development, administration, or collaboration. These issues can include bug reports, feature requests, discussions about database schema changes, or any other relevant topics. You can edit schema, change the data, add new database or add instance in Bytebase through this instance tab.
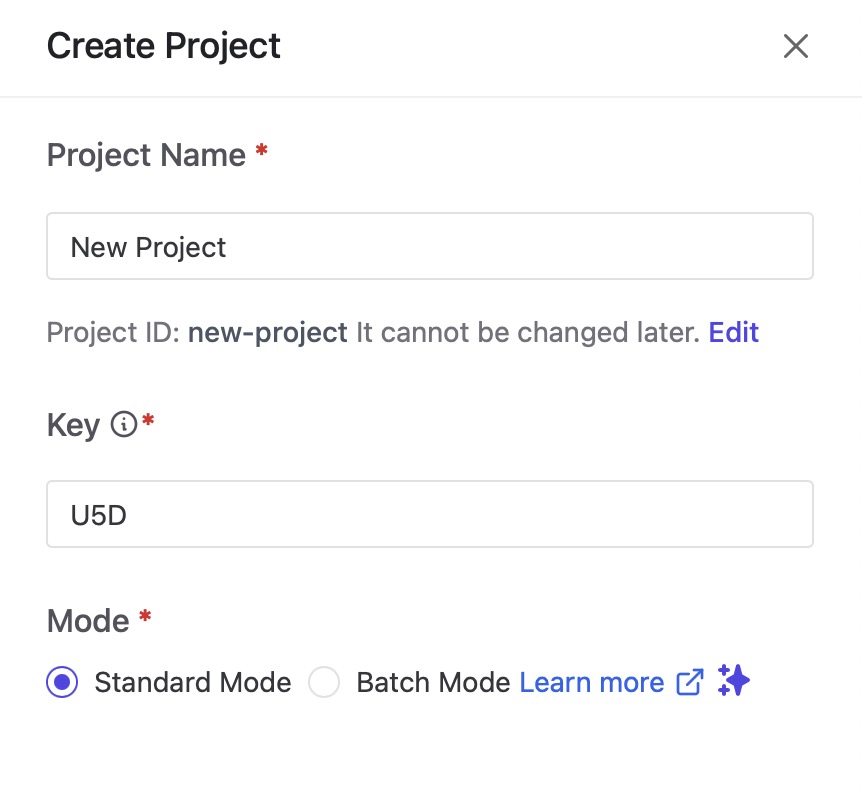
Create Project
In Bytebase, projects are organizational units or containers that help structure and manage database related tasks, activities, and collaborations. A project in Bytebase represents a specific database or a set of databases associated with a particular application or initiative. Within a project, users can organize and categorize various elements, such as tables, schemas, and issues, related to the database or databases involved. Click on "New Project" button to create a new project and provide the information like project name, key and mode.
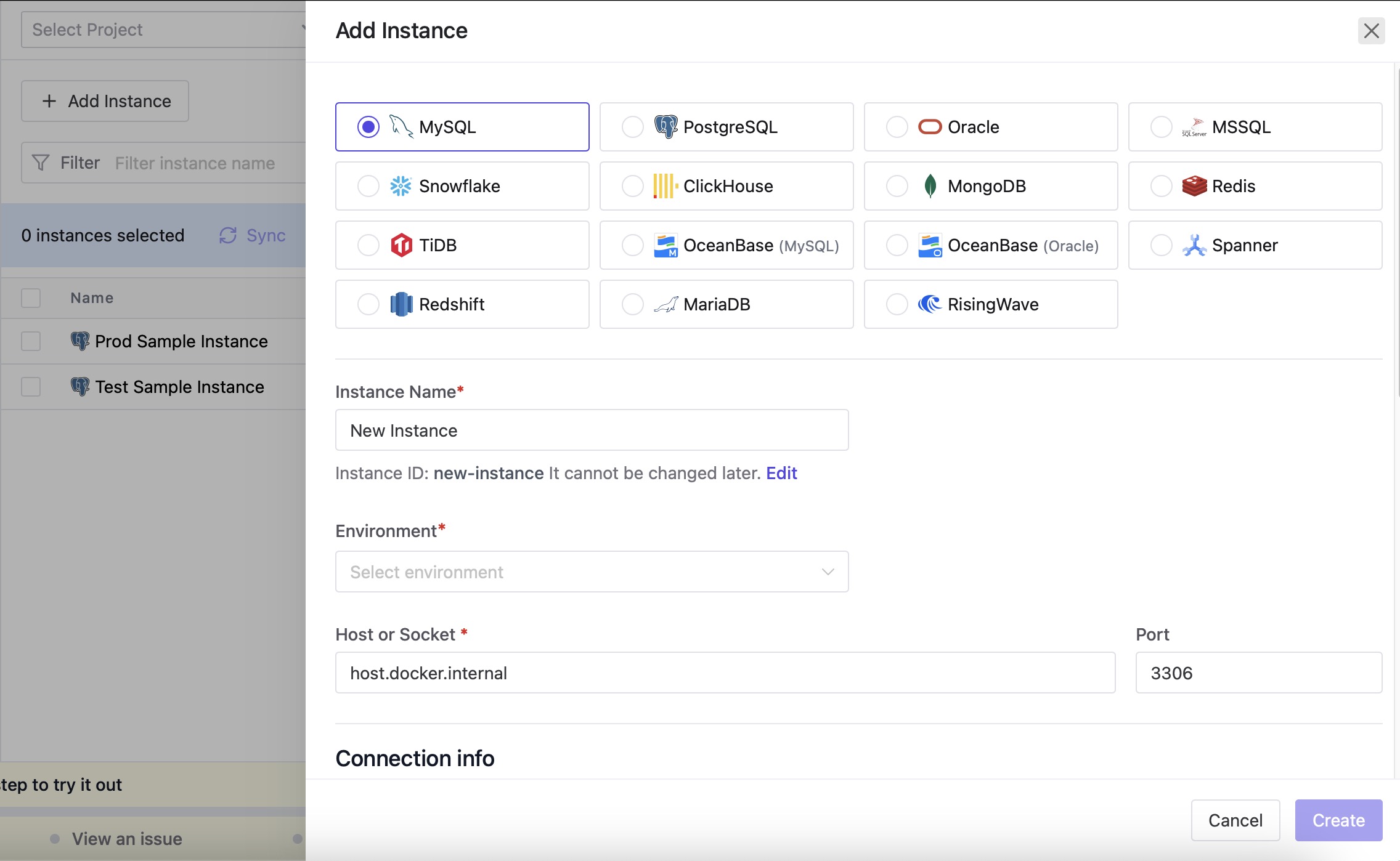
Add Instance
In Bytebase, an instance is an individual deployment or installation of the Bytebase database collaboration platform. Each instance is a self-contained environment that can be used by a team or organization to manage database related tasks. It includes its own set of databases, tables, schemas, and user permissions, providing a segregated space for organizing and working on specific database projects. Instances in Bytebase allow different teams or projects to operate independently, ensuring data isolation and security. Click on "Add Instance" and select the desired database, environment, host or sockets, ports and instance name to create a new instance.
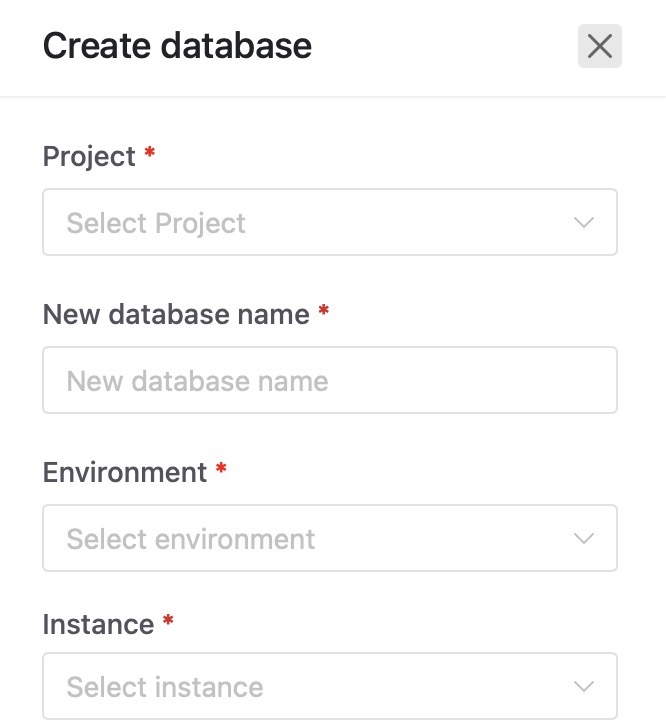
Create Database
In Bytebase, a database is a structured collection of data organized in a way that allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and management. Bytebase provides a collaborative environment for managing databases. Each database in Bytebase represents a logical grouping of related information, and users can interact with the data, execute queries, and collaborate with team members within the platform. For creating a new database head over to the Databases section from the left menu and click on "Create Database" button. Provide the database name, instance name and environment name to create a new database.
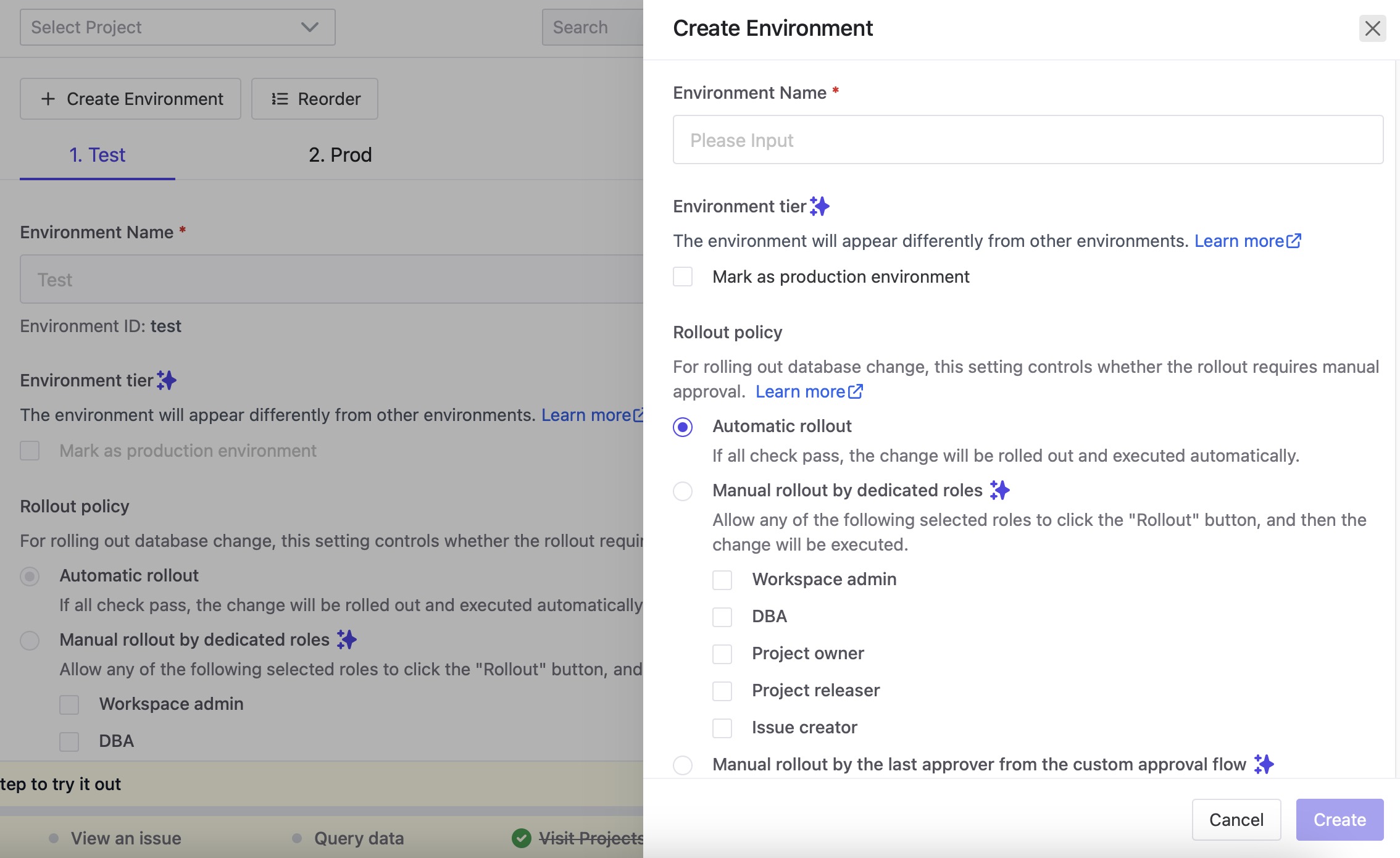
Create Environment
In Bytebase, special attention should be given to production environments. Administrators can designate an environment as a production environment in the Environment section of the environment detail page. You can manage, test and deploy your database in different environments. You can create a new environment by clicking on "New Environment" button and provide the environment name, description and color. Configure all the additional settings according to your environment requirements.
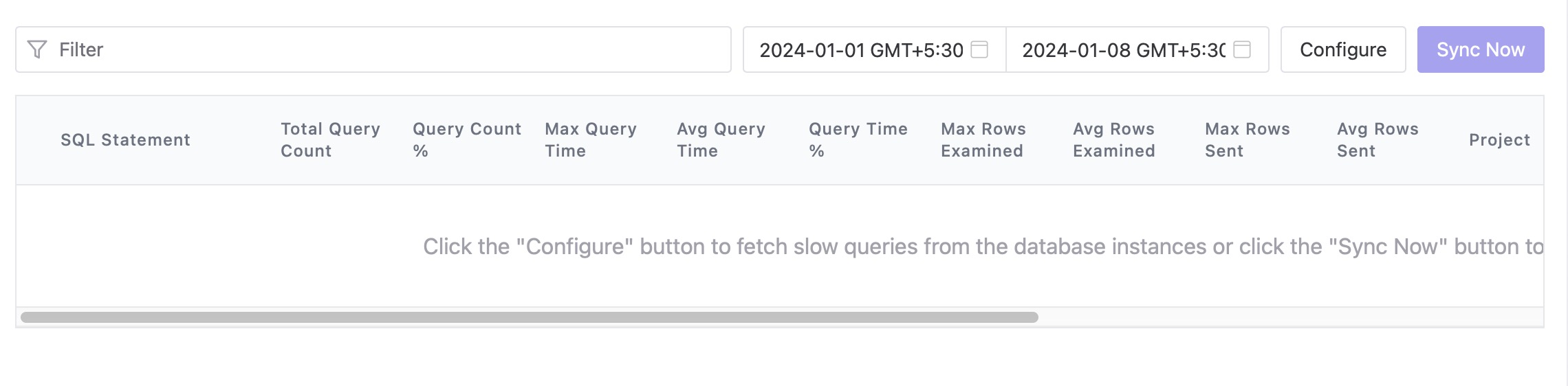
Slow Queries
The Slow Queries feature in Bytebase helps you identify and analyze slow queries in your database. This feature utilizes MySQL Slow Query Logs and PostgreSQL pg_stat_statements to provide insights into queries that are impacting the performance of your database. By identifying and optimizing slow queries, you can improve the overall efficiency and responsiveness of your database system. To checkout these queries, head over to the "Slow Queries" section from the left menu.
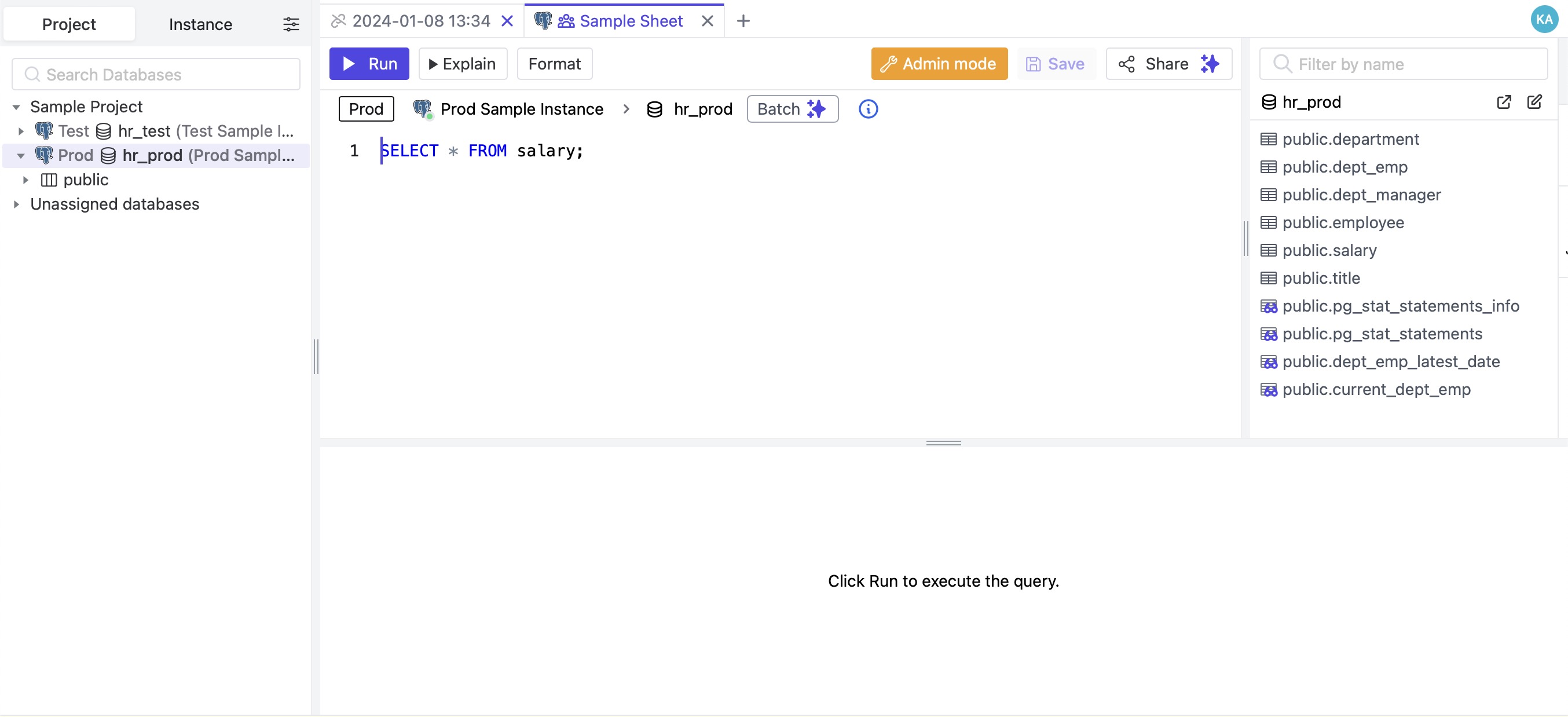
SQL Editor
The SQL editor in Bytebase is an interface enabling users to interact with their databases through SQL queries. It allows for the direct execution of SQL commands, facilitating tasks such as retrieving, modifying, and managing data within the relational databases connected to Bytebase. With features like syntax highlighting for improved readability, query history for reference, and result visualization in a tabular format. To access the SQL editor, click on the "SQL Editor" section from the navigation bar.
Settings
In Bytebase, Settings include a variety of configurable options that users can adjust to personalize their experience. These settings cover aspects such as user preferences, security configurations, integration preferences, appearance and theme customization, notification settings, database connection parameters, and access control features.