Mailcow is an open source platform for managing your email, simplifying the process of sending, receiving, and organizing messages. Mailcow helps in the process of managing your email system by providing a visual development environment that allows users to create and customize their email accounts and resources without writing code.
Login
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.
When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your email, name and password and click the "Login" button
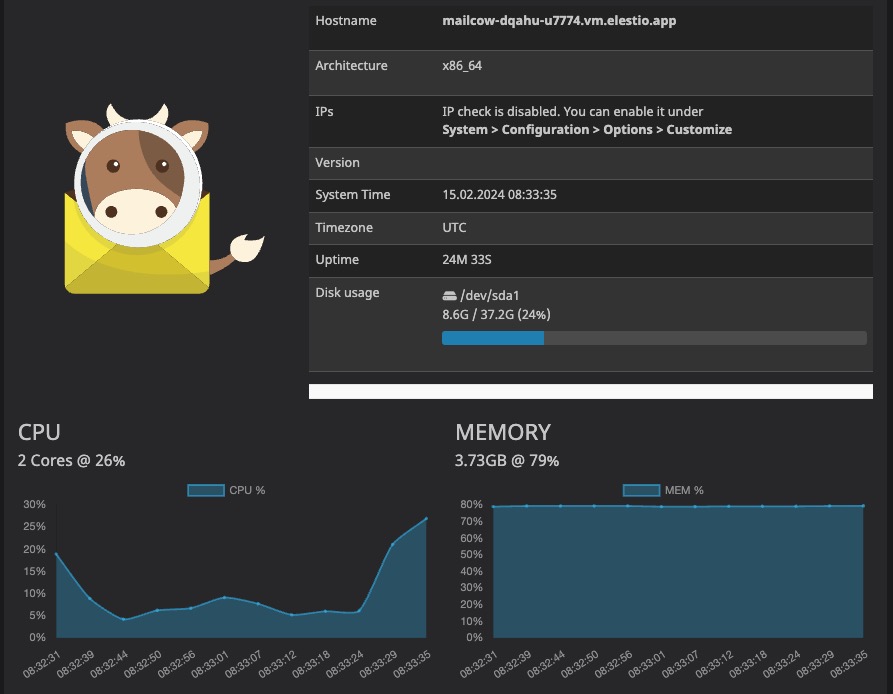
Dashboard
The dashboard in Mailcow is the main interface where you can manage various aspects of your email system. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows you to perform tasks such as managing mailboxes, resources, aliases, domains, synchronization, and viewing logs. You can view and manage cpu usage, memory usage, disk usage, and other system resources. The dashboard is a central component of Mailcow and serves as the primary interface for managing and monitoring your email system.
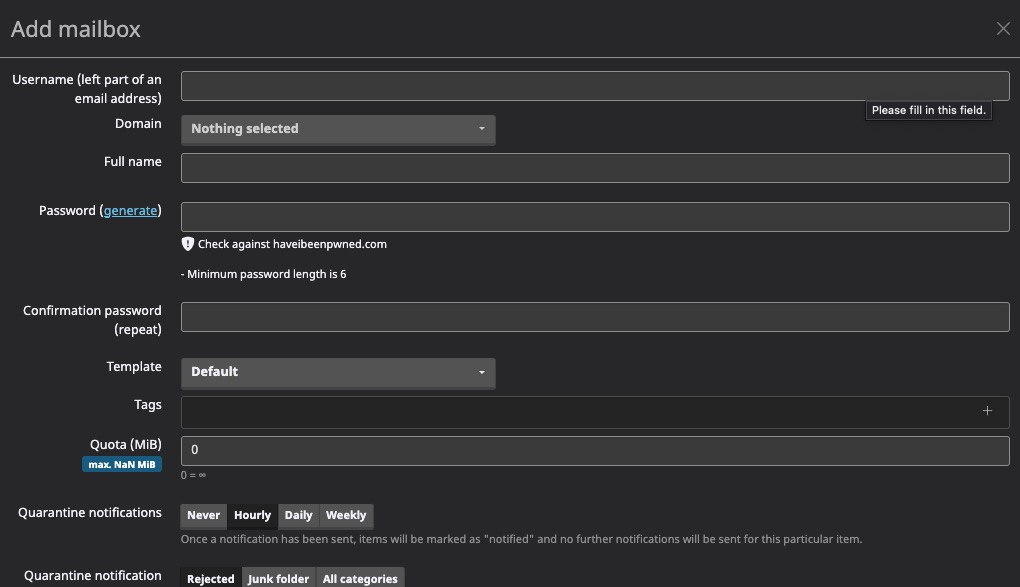
Adding Mailbox
Mailbox refers to an email account that is hosted on a Mailcow mail server. It allows users to send, receive, and manage their email messages. Adding a mailbox in Mailcow involves creating a new email account within the Mailcow email server. This typically includes specifying the desired email address, setting a password, and configuring any additional settings such as mailbox size limits or email forwarding rules. You can create a new mailbox by clicking on the "Add Mailbox" button.
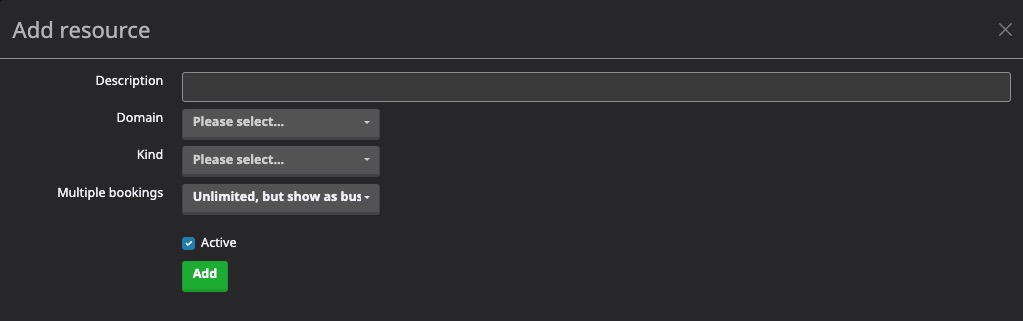
Adding Resource
Resource refers to any item or entity that can be accessed or manipulated within the mailbox. It could be an email message, a contact, a calendar event, or any other type of data that is stored or managed within the mailbox. The Resources section in Mailcow allows you to view and manage the resources associated with your mailbox, such as emails, contacts, and perform other actions related to resource management. This helps in keeping track of mailbox resources and ensuring that they are organized and accessible.
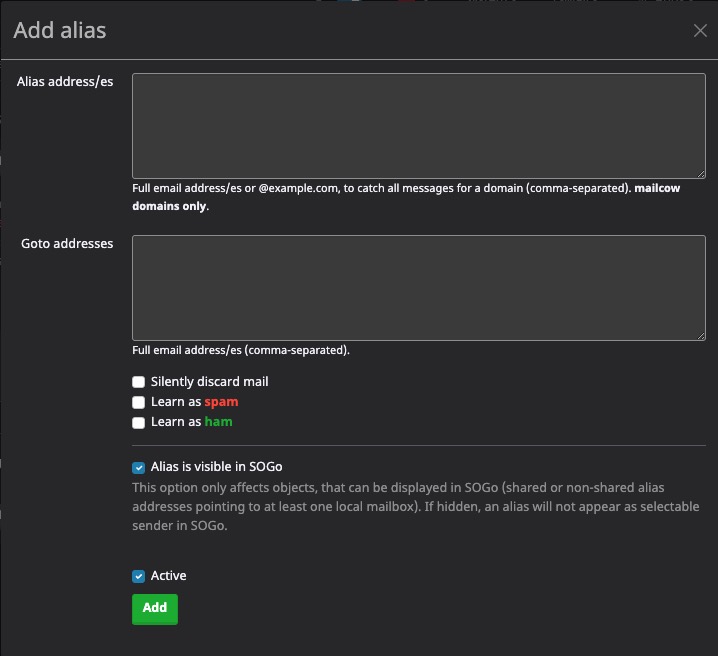
Adding Alias
An alias in Mailcow is an additional email address that is associated with an existing mailbox. It allows you to receive emails sent to the alias address and have them delivered to the original mailbox. Aliases can be useful for creating alternative email addresses or for organizing incoming emails. You can manage aliases in the Mailcow dashboard, where you can add, edit, or delete aliases for a specific mailbox.
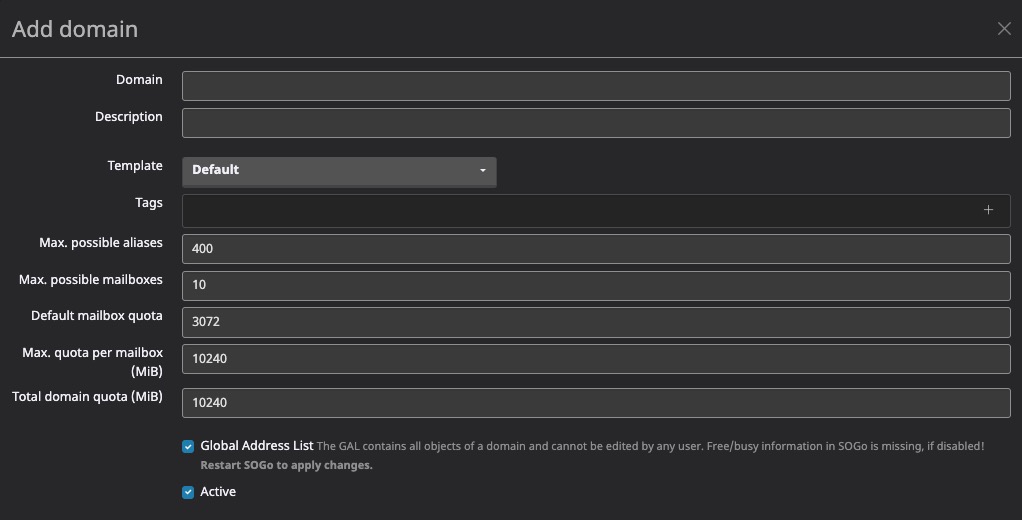
Adding Domain
Domain refers to the primary email domain that you own or manage. Domains in Mailcow are used to organize and manage email accounts and resources. You can add, edit, and delete domains in the Mailcow dashboard. Each domain can have multiple mailboxes, aliases, and resources associated with it. Domains play a crucial role in email delivery and routing. They help identify the destination of incoming emails and ensure that they are delivered to the correct mailboxes within your Mailcow instance.
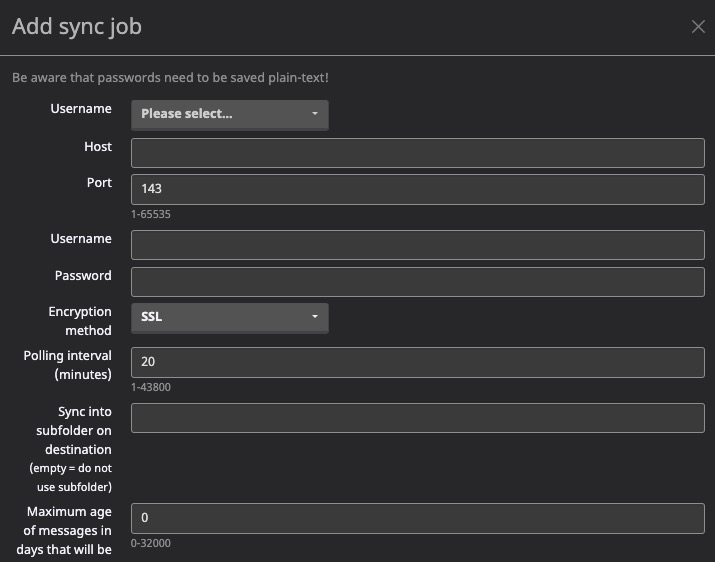
Adding Sync Job
Sync in Mailcow is the process of synchronizing email data between different devices or email clients. It ensures that changes made on one device are reflected on all other devices connected to the same email account. This includes syncing emails, contacts, calendars, and other resources. Mailcow supports various synchronization protocols such as IMAP, POP3, and ActiveSync, allowing users to access their email data across multiple devices and platforms.
Logs
Logs in Mailcow is the records or entries that capture information about the activities and events occurring within the Mailcow email system. These logs provide valuable insights into the system's performance, errors, and other relevant information. They can help administrators troubleshoot issues, monitor system health, and track user activities. The logs can include details such as email delivery status, error messages, login attempts, and more. You can view and analyze logs in the Mailcow dashboard to gain insights into the system's operation and identify any issues or anomalies.