Mastodon is a decentralized and open source social networking and a microblogging platform, allowing users to share short messages, images, videos, and links with their followers. This decentralized architecture helps user autonomy, data privacy, and community self governance, making it alternative to centralized social media platforms.
Log in
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.
When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your email, name and password and click the "Log in" button
Creating Posts
Posts are messages or updates shared by users on their profiles. These posts can contain text, images, videos, or links, and are typically referred to as "toots." Similar to tweets on Twitter, posts on Mastodon are visible to the users' followers and may appear in the timelines of others depending on visibility settings. Users can interact with posts by liking them, boosting , replying to them, or sharing them with others. Posts are a way for users to communicate and share content within the Mastodon social network. You can click on the "New Post" button to create a new post.
Explore
Explore allows users to discover new content and users across the network. It displays a curated selection of popular and trending posts, as well as recommendations for users to follow based on their interests and interactions. The Explore section helps users to explore beyond their immediate network, discover new communities, and engage with a wider range of content on Mastodon. It is a tool for discovering interesting content and connecting with like minded users across the platform. Users can head over to the "Explore" section to discover new content and users.
Live Feeds
Feeds are the streams of posts users encounter while navigating the platform. The home timeline displays posts from followed users, providing a personalized experience, while the local timeline showcases posts from all users within the same instance, fostering community interaction. The federated timeline aggregates posts from users across all Mastodon instances, offering a broader perspective on network wide conversations. These feeds enable users to stay informed about the latest updates from those they follow, discover new content within their community, and engage with diverse perspectives from across the Mastodon network.
Lists
Lists in Mastodon are a way to organize and group accounts that you follow. They allow you to create custom timelines that only show posts from specific accounts. This can be useful for organizing your feed based on different topics or interests. You can add or remove accounts from a list, and view the list's timeline to see posts only from those accounts. Lists provide a way to filter and focus on specific content within the Mastodon social network. You can add the list title and click on the "Add list" button to create a new list.
Bookmarks
Bookmarks allows users to save posts they find interesting or want to revisit later. When a user bookmarks a post, it's added to their list of saved items, accessible via their profile settings. Bookmarked posts remain private and are only visible to the user who saved them. This enables users to keep track of valuable or memorable content within the Mastodon platform, facilitating easy access to important posts or resources. Users can click on the "Bookmark" button to save a post to their bookmarks and access them later through bookmarks section.
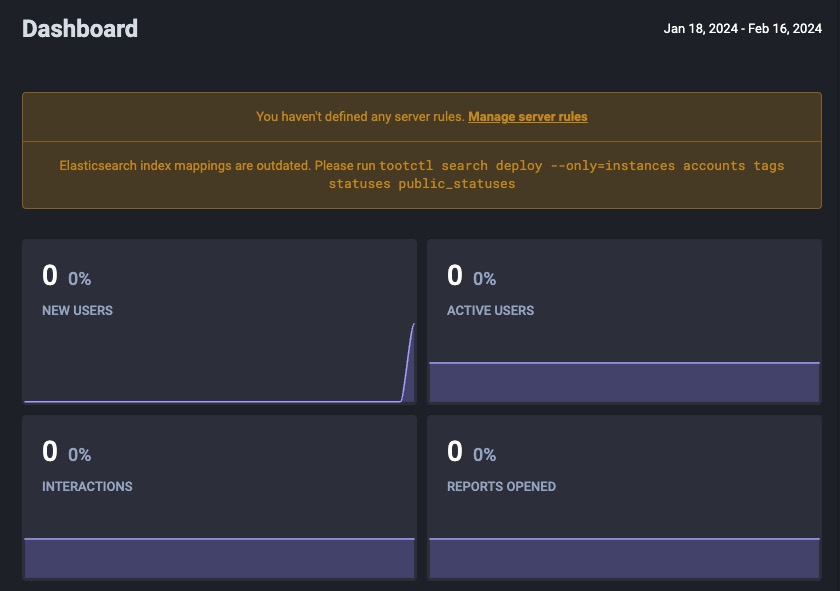
Dashboard
The admin dashboard in Mastodon is a centralized interface that allows administrators to manage and configure various aspects of their Mastodon instance. It provides tools and settings for managing users, moderating content, configuring instance settings, and monitoring the overall health and performance of the instance. Admins can see active users, new sign ups, and other statistics. The dashboard is a tool for administrators to maintain and optimize their Mastodon instance.
Webhooks
Webhooks in Mastodon are a way for external services to receive real time notifications about events happening on the Mastodon instance. When certain events occur, such as a new post being created or a user being followed, Mastodon can send a HTTP request to a specified URL, triggering the webhook. This allows developers to integrate Mastodon with other applications or services and automate actions based on these events. You can add endpoints by clicking on the "Add endpoint" button.