NocoBase is and open source tool that simplifies app development by eliminating the need for coding. With its interface, users can create a variety of digital solutions, from web pages to business tools. Creating dashboards or forms, NocoBase helps users to manage their data and create custom user interfaces.
Sign in
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.
When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your username and password and click the "Sign in" button.
Adding Page
In NocoBase, a page is a customizable user interface that allows you to interact with your data. You can design pages to display data, forms, charts, or other custom components. Each page can be tailored to present and manipulate data in a way that suits your application's needs. You might create a page to display a table of records from your database, complete with search, sort, and filter functionality. You could also design a page to present a form for creating or editing records.
Adding Group
a group typically refers to a collection of users who share the same set of permissions. Grouping users allows administrators to manage permissions more efficiently. Instead of assigning permissions to each user individually, the administrator can assign permissions to a group, and all users in that group will inherit those permissions. This makes it easier to manage access control, especially in larger organizations with many users.
Adding Link
Adding a link in NocoBase is creating a relationship between two tables. This is similar to creating a foreign key relationship in a relational database. Once the link is created, you can use it to navigate between related records, and to display related data in views and forms. This can make it easier to work with complex data structures and relationships. You can create a link by defining the fields that represent the relationship between the two tables.
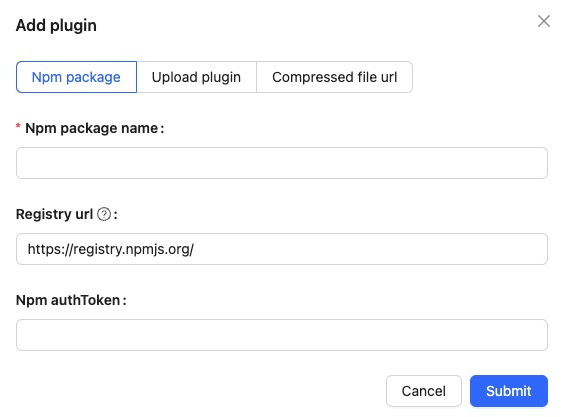
Adding Plugin
A plugin in NocoBase is a piece of software that adds extra functionality to the NocoBase platform. Plugins can extend NocoBase's capabilities, add new features, or customize its behavior. NocoBase plugins are developed using JavaScript and can be installed from the NocoBase plugin repository or from other sources. Once installed, a plugin's features become available for use within the NocoBase platform.
Backup & Restore
Backup and restore in NocoBase is the process of saving a copy of your NocoBase data and configuration (backup), and then being able to load that data back into NocoBase (restore) at a later time. The backup process involves exporting the data from your NocoBase tables to a file, which can be stored securely and used as a backup. This file contains all the data from your tables, as well as metadata about the table structure and relationships. The restore process involves importing the data from the backup file back into NocoBase. This can be used to recover your data if it's lost or corrupted, or to migrate your data to a new NocoBase instance.
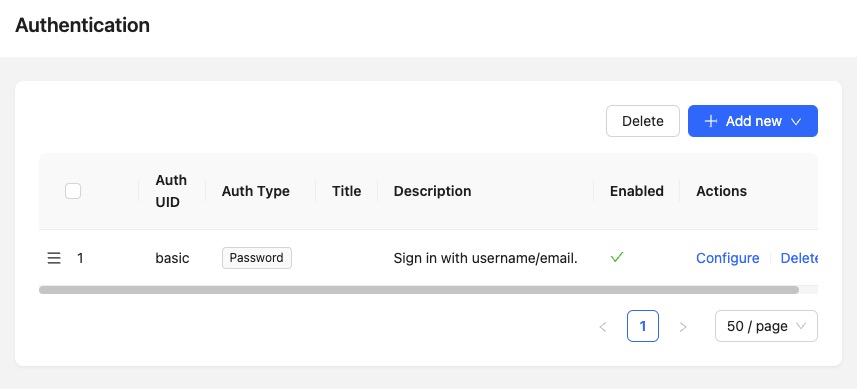
Authentication
Authentication in NocoBase is the process of verifying a user's identity. When a user tries to log in to NocoBase, they must provide their username and password. NocoBase checks these credentials against the stored user data. If the credentials match, the user is authenticated and granted access to NocoBase. NocoBase supports different methods of authentication. The default method is local authentication, where user credentials are stored and verified by NocoBase itself. NocoBase also supports third party authentication methods, such as OAuth and LDAP, where user credentials are managed by an external service.
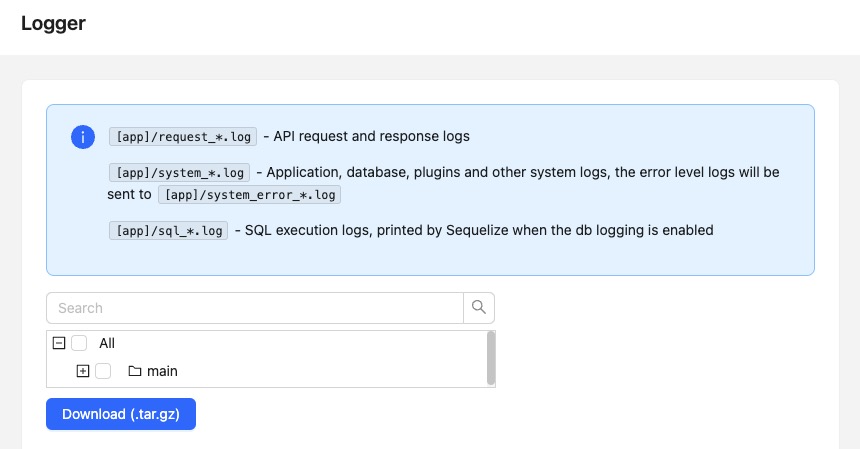
Logger
A logger in NocoBase is component that records events or transactions occurring within the system. These records, known as logs, can be used for debugging, monitoring system activity, auditing, and troubleshooting purposes. Logger might record events such as user logins, data modifications, system errors, and other significant activities. These logs can then be reviewed by system administrators or developers to understand the system's behavior, identify issues, or track changes.