OpenLDAP is an open source implementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). It is a platform for managing and organizing directory information, such as user accounts, groups, and other network resources. OpenLDAP is used for tasks like user authentication, authorization, and centralized management of user accounts and access control.
Login
On your first visit to the site, you will be presented with the login/signup screen.
When your instance is first created, an account is created for you with the email you chose. You can get the password for this account by going to your Elestio dashboard and clicking on the "Show Password" button.
Enter your username and password and click the "Login" button.
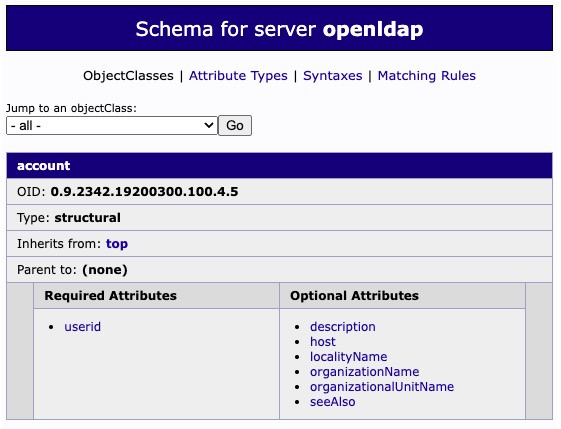
Schema For Server
Schema is a set of rules that define the types of objects and entries that can be created within an LDAP directory, and the attributes that those objects can have. A schema includes definitions for object classes and attributes. Object classes define the type of an entry, and each object class has a set of required and optional attributes. Attributes are characteristics of an object, such as a user's email address or a group's name. OpenLDAP comes with a set of standard schemas that define common object classes and attributes, but you can also add custom schemas to support specific needs. The schema ensures data consistency and integrity within the LDAP directory by enforcing the rules for data structure and format.
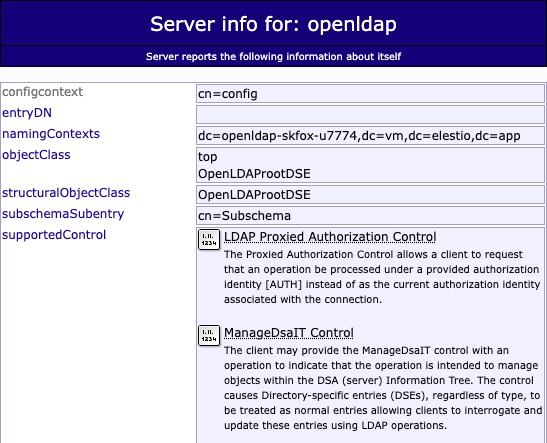
Server Info
Server is a program that manages and provides access to a directory of information. This directory is organized in a hierarchical and logical manner, similar to a tree, and can include details like usernames, addresses, phone numbers, and other relevant data. The OpenLDAP server uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to communicate with clients. Clients can perform operations like search, add, delete, and modify on the directory data. The server ensures that these operations are performed according to the rules defined in the LDAP schema and access control instructions.
Search
Search operation is a client-initiated action to retrieve entries from the LDAP directory based on specified criteria. The search operation includes a base DN (the starting point in the directory tree), scope (the extent of the search), filter (the conditions entries must meet), and attributes (the data to return for each entry). The OpenLDAP server checks access control rules, performs the search, and returns the matching entries to the client. This operation is fundamental to the usage of LDAP for tasks like user authentication, data retrieval, and more.
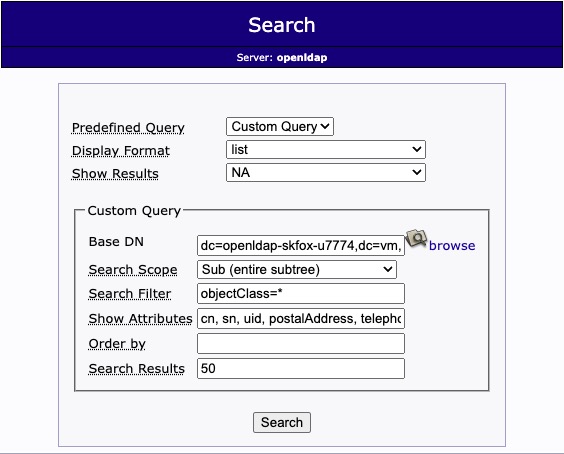
Import
Import is the process of adding data to the LDAP directory from an LDIF (LDAP Data Interchange Format) file. LDIF is a standard plain-text format for representing LDAP directory entries and updates. These utilities connect to the LDAP server, then add or modify entries based on the contents of the LDIF file. This import process is useful for tasks like initializing a new LDAP directory, migrating data from one LDAP server to another, or bulk updating directory entries. It's important to note that the user performing the import needs to have the necessary permissions to add or modify the directory entries.
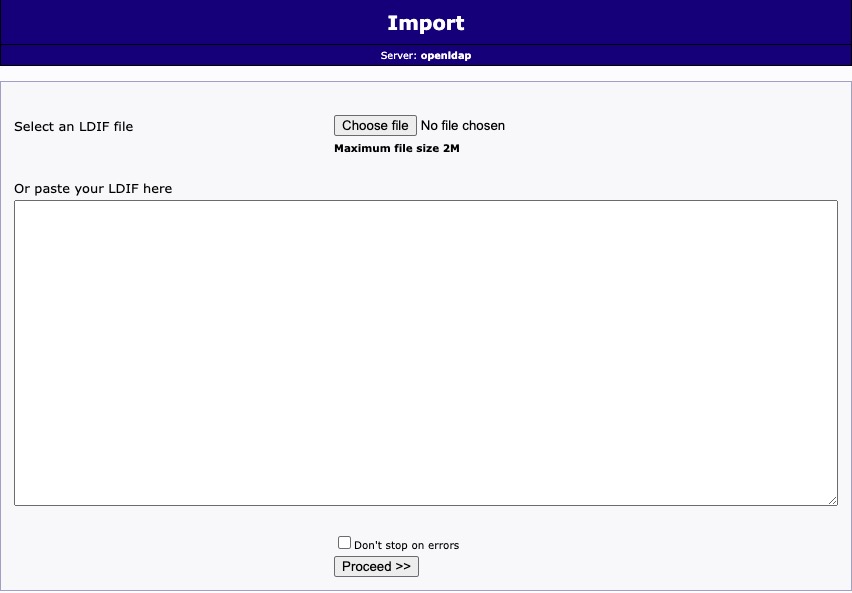
Export
Export refers to the process of extracting data from the LDAP directory and writing it to an LDIF (LDAP Data Interchange Format) file. LDIF is a standard plain-text format for representing LDAP directory entries and updates. This export process is useful for tasks like backing up directory data, migrating data to a new LDAP server, or analyzing directory data offline. It's important to note that the user performing the export needs to have the necessary permissions to read the directory entries.
Adding Attribute
Attribute is a piece of data associated with an entry in the LDAP directory. Each attribute has a name and one or more values. Attributes represent specific pieces of information about the object the entry represents. The types of attributes that an entry can have are defined by the object classes associated with the entry, and the available object classes and attributes are defined in the LDAP schema. Each attribute in the schema has a syntax that defines the type and format of its values.